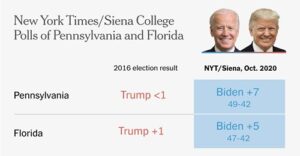
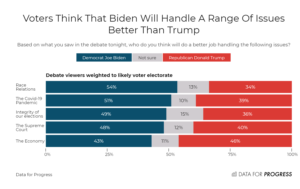
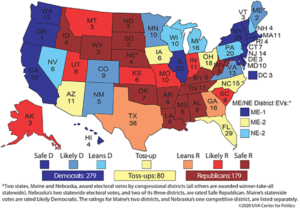
The following article by Ruy Teixeira, author of The Optimistic Leftist and other works of political analysis, is cross-posted from his blog:
I was intrigued to run across this piece by Michael Sean Winters “It’s time to bury the idea that demography is destiny, once and for all” in the National Catholic Reporter. He builds on my essay on this topic that appeared in Persuasion in July.
Surveys of Latino voters indicate something else that is worth noting: Demography is not destiny. Turns out this fact is worth noting again and again and again because the theory stalked much of the commentariat throughout the Democratic primaries and the selection of a vice presidential choice. In 2016, it was the theory that dominated the strategy of the Clinton campaign and left them scratching their heads as the election results poured in.
Ruy Teixeira and John Judis’ 2002 book, The Emerging Democratic Majority, is often credited with birthing this theory, but that excellent book was devoid of simplistic slogans. They noted that minority groups that tended to support Democrats were increasing their share of the electorate by 2% every four years. They never said the Democrats could ignore white, working-class voters.
In an essay at Persuasion, Teixeira argued that people misread the thesis of the book and, just as importantly, continued to misread the facts:
“Instead of focusing on the fact that this emerging majority only gave Democrats tremendous potential if they played their cards right, many progressives started to interpret it as a description of an inevitable future. The new Democratic majority, they believed, had already arrived. All they had to do to win election after election was to mobilize the growing segments of the electorate, and the demographic changes that favored them would take care of the rest. Sometimes explicitly, sometimes implicitly, our thesis turned into the simplistic argument that “demographics are destiny.”
The Obama coalition, remember, included enough white, working class-voters to comfortably win states like Pennsylvania and Iowa. Yet, in 2012, although Obama won reelection, his deficit among white, working-class voters doubled. The bailout of Wall Street never did trickle down to Wilkes-Barre. Teixeira explains:
“The bowdlerization of the emerging Democratic majority thesis neatly complemented the political predilections of a rising set of people who placed questions of group identity and disadvantage at the heart of their political activism. This approach, which soon came to be known as “identity politics,” privileges mobilization around multiple, intersecting levels of oppression based on group identification over mobilization around universal rights and principles that bind people together across groups. Since most white non-college voters were rightly perceived to be uninterested in — if not outright hostile to — the core tenets of intersectional politics, those who favored this approach had a reason to embrace an electoral strategy that dispensed with them.”
Soon enough, the candidate called them “deplorables,” and her schedulers never saw a reason to go to Wisconsin. The wishful demographic theory was combined with the meritocratic prejudices that Michael Sandel has so brilliantly diagnosed among America’s cultural leaders. The Democrats were — and are — unprepared for the populist backlash that Donald Trump rode into the White House, and that might carry him in a second time….
If you look at the research to which I linked in my article about polling Latinos, you will find that they articulate the same essential working-class concerns as white voters in Youngstown, Ohio: health care, job security, opportunities for their children, better schools. The New York Times article by Ian Haney López and Tory Gavito was especially on point, demonstrating the fact that core tropes of identity politics do not resonate with Latinos. They wrote that most Latinos declined to see themselves as “people of color,” that “the majority [of Latinos] rejected this designation. They preferred to see Hispanics as a group integrating into the American mainstream, one not overly bound by racial constraints but instead able to get ahead through hard work.” If Trump emphasizes the “white” in “white, working-class voters,” Democrats need to emphasize the “working-class.”
What does any of this have to do with our Catholic faith? It turns out, a lot. I wish I could tell you that the contempt for fellow citizens and for fellow Catholics epitomized by Hillary Clinton’s word “deplorables” was unique to her, but it isn’t. There is a cancer in the heart of the political left that has infected the Catholic left, too, and it is the cancer identified by Teixeira. The cancer is the “approach, which soon came to be known as ‘identity politics,’ [which] privileges mobilization around multiple, intersecting levels of oppression based on group identification over mobilization around universal rights and principles that bind people together across groups.”
It is a cancer because it does not unite — and culture always unites. The Catholic social teaching that formed Biden does not reduce people to their group because it starts with the universalist belief that we are all created in the image and likeness of God, and possessed of an inherent dignity. Biden would never call white, working-class voters, or anyone else, “deplorable.” Catholic social teaching balances the Gospel mandate to identify with the marginalized with this universalism that is at the heart of the Gospels, too.
Trump’s evil genius consists in his ability to accept the terms of identity politics and turn them to his own advantage. But let us be clear: His path has been cleared by those who traffic in identity politics, those who seek to denigrate any American ideal that strives for universality. Trump harvests grievances. He did not plant them. In his narcissism, he may not really give a damn about white, working-class voters. His economic policies — apart from trade — will not really help them. But he is never more sincere than when he shares their disgust with cultural and political elites who look down on working-class voters if they look at them at all. If one of the only things Democrats have to say to white working-class voters is that they suffer from white privilege, no one should be surprised if Pennsylvania and Wisconsin stay in the red column this year.
There is a reason that so much of the country stayed Democratic long after the New Deal: Franklin Roosevelt had created policies that helped them; he addressed their needs, and he never condescended to them. He gave them hope. In the absence of such hope, men like Trump, who offer only hateful and false answers to the problems many working-class cities and towns endure, will continue to win elections.”
Interesting. I am more optimistic than the author that Biden is making real progress among these voters in this election, perhaps especially white working class Catholics in Rustbelt states. But he is quite right that Democrats still have a long-term challenge convincing these voters that the party is committed to universal uplift that very much includes them.