In “Democrats have a huge opportunity to win back rural voters,” Christian Paz writes at Vox: “In last year’s midterms, when Democrats narrowly held on to control of the Senate and won crucial elections in battleground states, they did so in part by reversing one of Donald Trump’s biggest 2020 accomplishments: They won more voters from rural and exurban communities than anyone expected….From Arizona and Nevada, across the Midwest, and into North Carolina and Pennsylvania, Democratic Senate and gubernatorial candidates improved on President Joe Biden’s 2020 showing among this swath of the electorate, and persuaded tens of thousands of rural voters who voted for Trump to switch parties….Now, as the 2024 campaign map begins to take shape, Democratic candidates, the state and national parties, and their outside partners will have to make a choice about how seriously to invest in outreach and persuasion operations in these communities. Democrats have long struggled in rural communities, but their decline in support has only accelerated in recent years, cementing the idea for many that the party caters to highly educated and primarily urban voters. That narrative has only entrenched itself since the ’90s, when former President Bill Clinton essentially split rural voters with his Republican opponents in his two presidential campaigns and won over 1,100 rural counties in 1996. Since then, Democratic presidential candidates have endured dramatic losses in rural areas: in 2008, Barack Obama won 455 rural counties; in 2020, Joe Biden won only 194….That crumbling of rural support has led some in the party to write off this section of voters entirely. Biden’s 2020 victory is illustrative of this dynamic: He won the presidency despite winning just 33 percent of rural voters. (Trump won 65 percent, up from the 59 percent he won in 2016.)….But the 2022 midterms reversed that slide.”
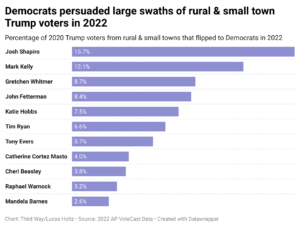
“The brightest spots for Democrats came in Michigan and Pennsylvania,” Paz continues, “where Gov. Gretchen Whitmer and Gov. Josh Shapiro, respectively, improved on Biden’s performance in rural counties by 10 and 15 percentage points. Candidates like Democratic Colorado Gov. Jared Polis, Sen. John Fetterman (D-PA), and Sen. Michael Bennet (D-CO) improved by more than 6 points — and even candidates who lost, like former Rep. Tim Ryan in Ohio’s Senate race, still improved on Biden’s numbers (winning 4 percent more support from these counties).” Paz shares the following chart:
Some troubling data points from “The End Of Title 42 Could Be A Big Problem For Biden” by Nathaniel Rakich at FiveThirrtyEight: “President Biden’s administration has been bracing itself for Title 42’s expiration by building more facilities for migrants, making it easier for people to apply to come to the U.S. legally rather than risk an illegal border crossing and even sending 1,500 troops to the border. And politically, taking such aggressive action is probably smart: Polling suggests not only that Americans want to keep Title 42 in place, but also that another border crisis could be a political disaster for Biden….According to a May 6-7 poll from Morning Consult, 51 percent of registered voters opposed ending Title 42, and only 37 percent supported ending it. While that’s the only recent poll we have on the subject, its findings were similar to those of a May 2022 poll from Politico/Harvard in which American adults opposed ending the program 55 percent to 45 percent….These numbers aren’t too surprising when you consider that a plurality of Americans thought too many immigrants were coming to the U.S. even before Title 42 expired. According to a February 2023 poll from the Associated Press/NORC Center for Public Affairs Research, 44 percent of U.S. adults thought the number of immigrants to the U.S. should be reduced. An additional 34 percent wanted the number of immigrants to remain the same, and only 20 percent thought it should be increased….In an average of six polls taken since April 18,2 only 35 percent of Americans said they approved of Biden’s handling of the issue of immigration, while 57 percent disapproved. That issue-specific net approval rating of -22 percentage points was 13 points worse than Biden’s average overall approval rating in those same polls….According to a Morning Consult poll from March, 47 percent of registered voters also felt that the U.S. immigration system had gotten worse under Biden’s presidency, while only 20 percent thought it had gotten better (24 percent said it had stayed the same).”
Rakich observes in “Other Polling Bites,” also at FiveThirtyEight, that “Americans may finally be coming to understand what the debt ceiling finally means, after more than a decade of high-profile fights over it. A new YouGov survey explained the debt ceiling to half of its sample and then asked them their opinion on raising it, while it just asked the other half about raising it without any context. In both cases, roughly 40 percent said that the debt ceiling should be raised and roughly 40 percent said that it should not. In addition, 52 percent correctly identified the debt ceiling as a limit on the government’s borrowing to finance spending that already has been approved, while only 25 percent incorrectly said it was a limit on government spending. Compare this to a similar YouGov poll from 2013, when 42 percent said raising the debt ceiling would allow the U.S. to pay interest on its debt and for spending that it has already authorized, and 39 percent said it would directly increase government spending and debt.” There may be a bit of a “Boy Who Cried Wolf” trope regarding the public’s tendency to yawn about the debt ceiling fight, which has always seemed to get resolved at the last minute. That doesn’t make it any less of a problem for president Biden. Indeed, it may make it more dangerous. In any case, it’s not a good look for either party, and a permanent fix would serve them both well.



